1. Introduction to Injection Molding
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for creating parts by injecting molten material into a mold. This method is primarily known for producing plastic components but can also be used with metals and other materials. The process is fundamental to modern manufacturing, allowing for high-volume production of complex shapes and components with excellent precision.
Essentially, the injection molding process starts with melting the material, typically in granular form, and injecting it into a pre-designed mold under high pressure. Once the material cools and solidifies, the mold is removed, revealing the final product. This technique has revolutionized the way products are designed and produced, offering advantages in terms of efficiency, quality, and repeatability.
For further information on injection molding, it’s vital to understand its history and applications across different industries.
The History of Injection Molding
The history of injection molding dates back to the 19th century, with the first injection molding machine being patented by John Wesley Hyatt in 1872. Originally designed to mold billiard balls from a material called celluloid, the process has significantly evolved since then.
In the mid-20th century, advancements in technology and the introduction of thermoplastics transformed injection molding into a viable option for mass production. As plastic materials became more versatile and affordable, industries began to recognize the potential for large-scale production of consumer goods, automotive components, and medical devices.
Applications in Various Industries
Injection molding finds applications across a diverse range of industries, including:
- Automotive: Used to manufacture parts like dashboards, panels, and housings.
- Consumer Goods: Produces everyday items such as utensils, containers, and toys.
- Medical Devices: Critical for creating components in surgical tools, syringes, and diagnostic equipment.
- Electronics: Production of casings, connectors, and insulation components.
2. Understanding the Injection Molding Process
Stages of Injection Molding
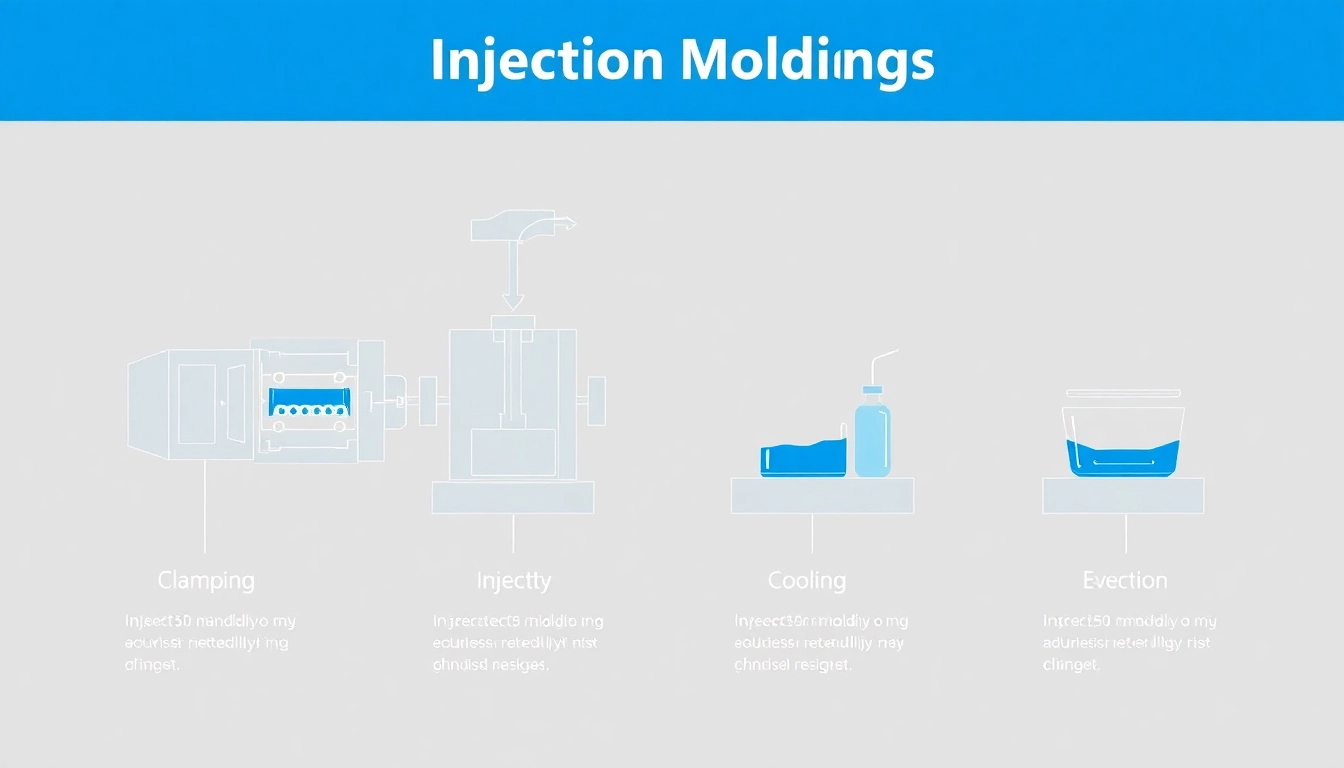
The injection molding process involves several key stages that must be carefully executed to ensure high-quality products:
- Clamping: The mold is securely closed, ensuring that no material escapes during injection.
- Injection: Molten material is injected into the mold at high speed and pressure.
- Cooling: The material cools and solidifies inside the mold, taking the shape of the cavity.
- Ejection: Once cooled, the mold opens, and the finished product is ejected.
Materials Used in Injection Molding
There are numerous materials suitable for injection molding, each with distinct properties:
- Thermoplastics: The most common choice, these materials become pliable when heated and solidify upon cooling. Common examples include polyethylene and polypropylene.
- Thermosetting Plastics: These materials harden when heated and cannot be remelted. They’re often used for high-heat applications.
- Elastomers: These are rubber-like materials providing flexibility and durability, used in products like seals and gaskets.
Common Equipment for Injection Molding
The injection molding setup involves several essential equipment pieces:
- Injection Molding Machine: This machine melts the material and injects it into the mold.
- Molds: Custom-designed for each product, molds shape the melted material.
- Chiller Units: Used to cool the mold and enhance production efficiency.
3. Advantages of Injection Molding
Cost Efficiency and Mass Production
One of the standout benefits of injection molding is its cost-effectiveness, especially regarding large-scale production. Once a mold is fabricated, it can be used to produce thousands of identical parts, significantly reducing the manufacturing cost per unit. This efficiency makes it an excellent option for mass production.
Design Flexibility and Precision
Injection molding offers designers remarkable flexibility in creating intricate shapes and fine details. Molds can be tailored to complex designs, allowing the production of parts with varying thicknesses and geometries. The precision with which molds are made ensures a high dimensional accuracy of the final products.
Environmental Considerations and Recycling
With the increasing focus on sustainability, injection molding has adapted by utilizing recyclable thermoplastics, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process. Moreover, the closed-loop systems often used in injection molding can minimize waste and energy consumption.
4. Challenges and Solutions in Injection Molding
Common Defects and How to Avoid Them
While injection molding is an effective manufacturing process, it is not without challenges. Common defects include:
- Warpage: Caused by uneven cooling, leading to distortion of the final product. This can be minimized by optimizing cooling systems.
- Short Shots: Occurs when insufficient material fills the mold. Ensuring proper material flow can help avoid this issue.
- Surface Defects: Imperfections in the mold can transfer to the product surface. Regular maintenance can prevent this problem.
Material Selection Challenges
Selecting the right material for the product is crucial. Factors such as the product’s intended use, mechanical properties, and environmental conditions must be considered. Utilizing simulation software can help predict material behavior and select the most suitable options for specific applications.
Optimizing Cycle Times
Cycle time optimization involves reducing the total time taken for the molding process. This can be achieved through multiple strategies, such as:
- Improving cooling techniques.
- Using faster machines and molds.
- Streamlining the production workflow.
5. Innovations and Future Trends in Injection Molding
Smart Technologies in Injection Molding
The adoption of smart technologies, such as IoT and automation, is transforming the injection molding sector. These technologies promise enhanced machine monitoring, predictive maintenance, and data management, resulting in better productivity and efficiency.
3D Printing Influence on Injection Molding
3D printing is beginning to change the landscape of injection molding by allowing quicker prototyping and the potential for creating complex molds at a lower cost. This technology can also work in tandem with injection molding to enhance product design flexibility.
Global Market Trends and Future Outlook
As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, the injection molding market is expected to grow, with a particular emphasis on eco-friendly materials and processes. Innovations that streamline the production process and enhance product quality will sustain interest and investment in this manufacturing technique.











Leave a Reply