Understanding the Manufacture of Plastic Parts
The manufacture of plastic parts is an essential component of modern industry, providing the building blocks for a multitude of products that consumers interact with daily. From automotive components to electronic enclosures, plastic parts have revolutionized manufacturing due to their lightweight, durable, and versatile properties. Understanding the intricacies of plastic part manufacturing is vital for businesses aiming to enhance productivity, improve quality, and reduce costs.
What are Plastic Parts and Their Uses?
Plastic parts are any components made from plastic materials through various manufacturing processes. These parts are utilized across a myriad of applications, including:
- Automotive: Bumpers, dashboards, and interior fittings are often made of lightweight plastics to improve fuel efficiency.
- Consumer Electronics: Housing for smartphones, televisions, and computers are frequently composed of molded plastic for its durability and design flexibility.
- Medical Devices: Medical trays, syringes, and other devices often utilize bio-compatible plastics to ensure safety and performance.
- Packaging: Plastic is pervasive in packaging solutions for food, beverages, and pharmaceuticals due to its lightweight nature and barrier properties.
These diverse applications illustrate just how ingrained plastic manufacturing is within modern society.
The Importance of Quality in Plastic Manufacturing
Quality control in the manufacture of plastic parts is critical. It impacts product performance, safety, and customer satisfaction. To ensure high quality, manufacturers employ various standards and techniques, including:
- Material Verification: Utilizing high-grade raw materials appropriate for the intended application prevents early degradation or failure.
- Process Control: Regular monitoring of manufacturing processes reduces defects and inconsistencies.
- Final Inspection: Rigorous testing of finished products, including dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional testing, ensures they meet the specified criteria.
By achieving and maintaining high quality, manufacturers can better meet regulatory requirements and enhance overall product reliability.
Key Factors in the Manufacture of Plastic Parts
Several critical factors play a pivotal role in the successful manufacture of plastic parts:
- Design Complexity: The complexity of a part dictates the manufacturing method and tooling required, impacting costs and timelines.
- Cost of Materials: The choice of resin and additives affects both performance characteristics and production costs.
- Environmental Considerations: Sustainable practices in material sourcing and energy consumption have become increasingly important for manufacturers.
- Technological Advancements: Automation, CAD/CAM technologies, and rapid prototyping techniques significantly contribute to improved efficiency and accuracy.
Popular Methods for Manufacturing Plastic Parts
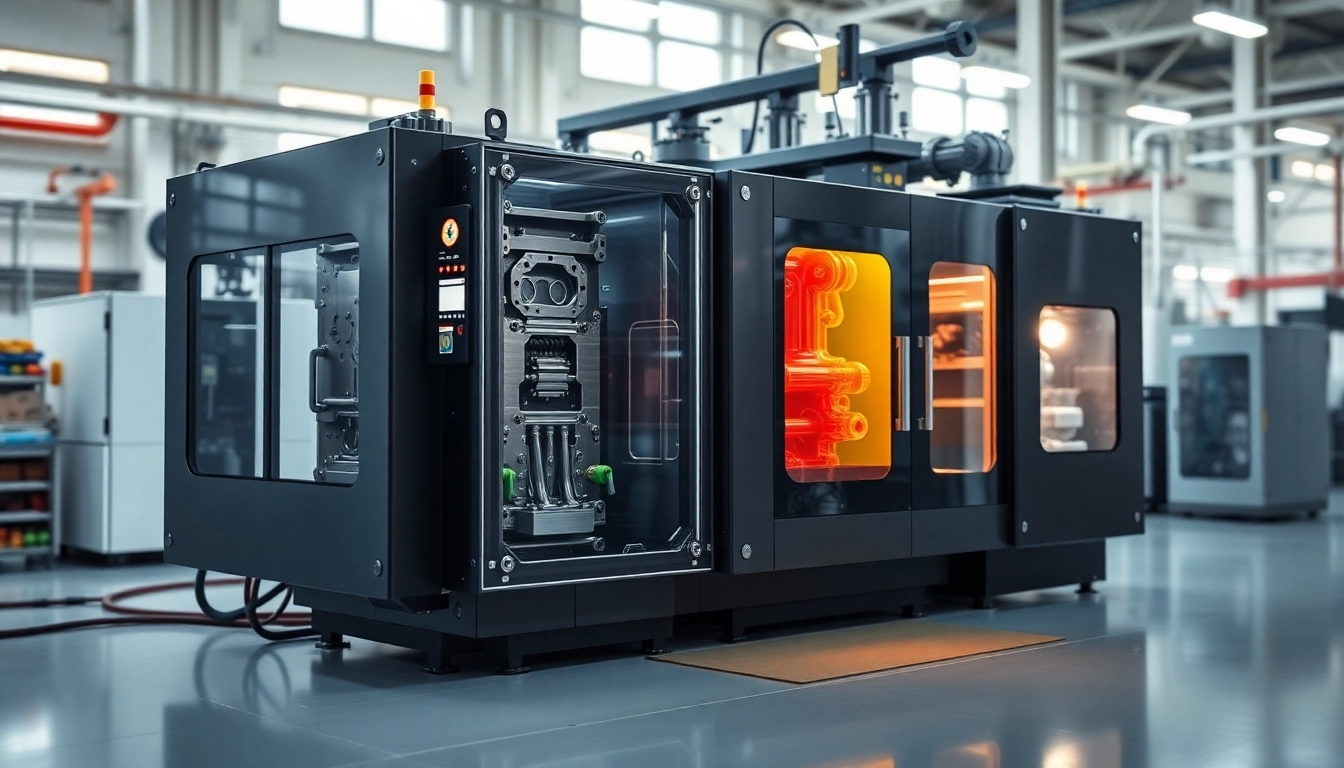
Injection Molding: The Industry Standard
Injection molding is the most commonly employed method for producing plastic parts, particularly for high-volume productions. In this process:
- Plastic material is heated until it becomes molten.
- The molten plastic is injected into a precisely designed mold.
- After cooling, the mold is opened, and the molded part is ejected.
This technique is favored for its ability to produce intricate designs with excellent tolerances and repeatability. Notably, injection molding is suitable for a wide range of thermoplastics and thermosets, making it applicable in various sectors.
Alternatives to Injection Molding
While injection molding is prevalent, several other methods may be preferable based on specific application requirements:
- Blow Molding: Ideal for hollow plastic parts, such as bottles, this method involves inflating a hot plastic tube within a mold.
- Thermoforming: Here, plastic sheets are heated and formed over a mold, commonly used for packaging and consumer products.
- Rotational Molding: Typically used for large, hollow objects, this method involves rotating a mold filled with powder resin.
- 3D Printing: This additive manufacturing method creates parts layer by layer, allowing for rapid prototyping and customization.
Emerging Technologies in Plastic Manufacturing
The plastic manufacturing landscape is continually evolving, driven by technological advancements. Key trends include:
- Smart Manufacturing: Integration of Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time monitoring and control, allowing for enhanced operational efficiency and predictive maintenance.
- Sustainable Practices: Development of biodegradable plastics and recycling technologies aimed at reducing environmental impact.
- Digital Twin Technology: Utilization of virtual models to simulate manufacturing processes, enabling improved design and troubleshooting.
Choosing the Right Materials for Plastic Parts
Common Materials Used in Plastic Manufacturing
Plastic materials can be broadly categorized into thermoplastics and thermosets, with each category encompassing a variety of types based on specific properties:
- Polypropylene (PP): Known for its flexibility and chemical resistance, widely used in packaging and automotive parts.
- Polyethylene (PE): Highly versatile and lightweight, employed in everything from plastic bags to containers.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Renowned for its durability, commonly used in construction products, electrical cable insulation, and more.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Excellent impact resistance, often used in eyewear lenses and safety equipment.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): A tough and resilient material favored for its aesthetic appeal in consumer products.
How Material Choice Affects Part Performance
The selection of materials in plastic manufacturing significantly influences part performance and suitability for specific applications. Considerations include:
- Mechanical Properties: Tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility characteristics determine durability.
- Thermal Resistance: Ability to withstand temperature fluctuations without deformation is crucial in automotive and electronic applications.
- Chemical Compatibility: Resistance to solvents and acids is vital for parts used in industrial contexts.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The ability to achieve desired colors, finish, or textures can influence consumer choice, especially in retail environments.
Sustainability in Plastic Material Selection
With growing concerns over environmental impact, sustainable material choices are crucial for modern manufacturers. Options include:
- Recycled Plastics: Utilizing materials that have been reclaimed reduces waste and dependency on virgin resources.
- Biodegradable Plastics: These materials break down more effectively than traditional plastics, offering a potential solution to long-term waste issues.
- Biobased Plastics: Sourced from renewable biomass, these materials provide an alternative to petroleum-based plastics.
The Manufacturing Process Step-by-Step
Preparing for Production: Designing the Mold
The design phase is critical in the manufacturing process of plastic parts. This includes:
- Mold Design: CAD software is used to create the mold design, considering factors such as part complexity and material flow.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate resin based on part application and performance requirements.
- Prototype Testing: Producing prototypes to test form, fit, and function before full-scale production begins.
Executing the Manufacturing Process
Following mold preparation, the actual manufacturing process involves multiple stages:
- Mold Setting: Setting up the injection molding machine and ensuring all parameters are correctly calibrated.
- Injection: The molten plastic is injected into the mold under high pressure to fill all cavities.
- Cooling: Parts are cooled in the mold to solidify before ejection, which allows them to maintain their shape.
- Ejection: Finished parts are carefully removed from the mold without causing damage.
Post-Production Quality Control Measures
Quality control post-manufacturing entails verifying that parts meet required specifications:
- Dimensional Inspection: Measuring parts to ensure they fall within tolerances set during design.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, color consistency, and overall aesthetics.
- Functional Testing: Testing parts in real-world conditions to ensure they perform as intended.
Future Trends in Plastic Part Manufacturing
Automation and Its Impact on Production Efficiency
Automation is set to play a major role in the future of plastic part manufacturing. Implementing robotics in production lines provides numerous benefits, including:
- Increased Speed: Machines can operate continuously and with precision, reducing lead times.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automation minimizes the need for manual labor in repetitive tasks.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated systems reduce human error, resulting in higher quality products.
3D Printing in Plastic Parts Manufacture
3D printing technologies are changing the paradigm of plastic manufacturing by enabling:
- Rapid Prototyping: Quick iterations in design allow for faster development cycles.
- Customized Solutions: Tailored parts can be produced in small batches without significant investment in tooling.
- Complex Geometries: Additive manufacturing can achieve intricate shapes that traditional methods cannot, expanding design possibilities.
Adapting to Environmental Regulations in Manufacturing
As environmental concerns and regulations tighten, plastic manufacturers must adapt to stay compliant. Key strategies include:
- Material Innovation: Developing and utilizing eco-friendly materials that meet performance standards.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving technologies and practices to minimize carbon footprints.
- Compliance Training: Ensuring all employees understand and adhere to regulations and best practices related to sustainability.












Leave a Reply